Contents
Overview
Features
* Created in 2005
* Fully distributed
* Fast and efficient with large projects
* Incredible branching system for non-linear development (thousands of parallel branches)
Diff from CVCS (Centeralized VCS)
* GIT keeps file snapshots not deltas (such as SVN)
* Nearly every operation is local (no need for network connectivity)
* Everything is checksumed (by SHA-1) before being installed
* Uses object database (not relational db) called object store
Object Store
* Object store contains three types of objects:
– blob: represents a file
– tree: represents a directory
– commit: represents a snapshot of the entire repository content
– annotated tags: human readable object associated with a particular commit
* Git objects are stored in .git/objects folder
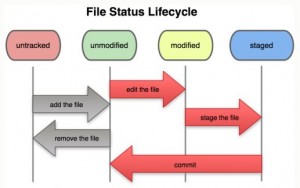
File Status
* Unstaged: not under Git control
* Staged: added to Git control, e.g. command git add file.txt stages file.txt file.
* Committed: added to Git control, e.g. command git commit -m “Commit message” file.txt adds file.txt file got Git control.
Checking File Status
* git status
$ git status On branch master nothing to commit, working tree clean
Three Config Files
* /etc/gitconfig
– System wide configuration
– For all users and all repositories
git config --system
* ~/.gitconfig
– User specific configuration
git config --global # Edit global configuration git config --global --edit
* .git/config
– Config file in the git directory
– For single repository
– Take precedence over ~/.gitconfig over /etc/gitconfig
Install
Windows Install
* Download from git download site, e.g. Git-1.8.4-preview20130916.exe
* Double click to install, accept all defaults
* Open git shell: All Programs > Git > Git Bash
Linux Install
* yum install git-core
* yum install git
First Time Setup
* Setup user identity
git config --global user.name "Jimmy Li" git config --global user.email jimmy.li@yahoo.com
* Setup editor (defaults to vi)
git config --global core.editor vim # For Git-for-Windows 2.5.3 and above git config --global core.editor notepad
* Setup diff tool
git config --global merge.tool vimdiff
* Setup aliases
git config --global alias.co checkout git config --global alias.br branch git config --global alias.ci commit git config --global alias.st status git config --global alias.lg "log --pretty=oneline"
* Check config:
git config --list
$ git config --global user.name "Jimmy Li" $ git config --global user.email jimmy.li@yahoo.com $ git config --list user.name=Jimmy Li user.email=jimmy.li@yahoo.com alias.co=checkout alias.br=branch alias.ci=commit alias.st=status alias.lg=log --pretty=oneline
Ignore Files
* Ignore files: place ignore rules in .gitignore file
* Rules:
Blank lines or lines starting with # are ignored. Standard glob patterns work. You can end patterns with a forward slash (/) to specify a directory. You can negate a pattern by starting it with an exclamation point (!).
* Examples:
# a comment - this is ignored # no .a files *.a # but do track lib.a, even though you're ignoring .a files above !lib.a # only ignore the root TODO file, not subdir/TODO /TODO # ignore all files in the build/ directory build/ # ignore doc/notes.txt, but not doc/server/arch.txt doc/*.txt # ignore all .txt files in the doc/ directory doc/**/*.txt # Ignore Thumbs.db Thumbs.db # Ignore $tf folders tfs/DEV/$tf*/ # Ignore all folders in Java folder # but not ant and config subdirectories tfs/DEV/Java/* !tfs/DEV/Java/ant/ !tfs/DEV/Java/config/
Help
git help <command> git <command> --help man git-<command> e.g. git help config
Basics
Getting a Git Repository
* Initialize a Repository in an Existing Directory
# Creates a git repository in current directory # Also setup current directory as working directory git init # Creates a git repository named my-proj.git without working directory # Use this for a central repository git init --bare my-proj.git
* Cloning an Existing Repository. Usually we clone from a central repository to work on.
git clone [url]
* git url formats:
git:// http(s):// user@server:/path.git # Local path --local file:///C:/path/to/repo/my_project
* Example
# Clone a central repository git clone file:///w/git/test2/my-proj.git
# Clone Azure DevOps using personal auth token $MyPat = 'xxx' $B64Pat = [Convert]::ToBase64String([System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetBytes("`:$MyPat")) git -c http.extraHeader="Authorization: Basic $B64Pat" clone devops_git_url
Recording Changes to the Repository
* Check file status:
git statusStage Files
* Add new files to stage area:
# Add a particular file git add file1.txt # Add current directory and all its content to stage area: git add . # Add a particular directory git add com.acme # Add all changed and deleted files but not new files git add -u # Add all files including new files git add -A # Interactive add git add -p
Un-Stage Files
* Remove staged files
# Unstage all staged files git reset # Unstage a particular staged file git reset file1.txt git reset HEAD file1.txt # Interactive unstage git reset --patch # Reset to remote and discard all local changes. Be careful! git reset --hard origin/master
View Changes
* View un-staged, i.e. have not being git add, changes:
git diff web.config* View staged, i.e. have been git add changes:
git diff --staged web.config
* View diff between any two files:
git diff a/web.config b/web.config
* View diff between any two commits:
git diff b7b382a3 f31018af // Display diff for all files between two commits git diff b7b382a3 f31018af web.config
Commit Changes
* Commit staged changes:
# Commit all staged files git commit -m 'Commit staged files.' # Commit a particular staged file git commit -m 'Add file1.txt.' file1.txt
Remove Files
* Remove file1.txt from git,
– also remove it from working directory:
git rm file1.txt # Need to commit to make it into Git git commit -m "Remove fil1.txt." file1.txt # Log git log --pretty=oneline d546e7cee2d190d1a063735dad91584734d1268c Remove fil1.txt. 17b6750215ba69a7dd132a4469fcfdaa01262d80 Add file1.txt
* Examples:
# Remove all .log files git rm log/\*.log git commit -m "Remove all log files in log directory."
Moving Files
git mv from_file to_fileView Commit History
git log git log -p # show diff git log -p -2 # show diff of last two entries git log --stat git log --pretty=oneline # others: short, full, fuller git log --pretty=format:"%h - %an, %ar : %s" # Use custom format git log --pretty=format:"%s %s" --graph # Use graph git log --since=2.weeks git log --pretty="%h - %s" --author=gitster --since="2008-10-01" \ --before="2008-11-01" --no-merges -- t/ # Show reflog git log -g --pretty=oneline
* Launch log history in GUI:
gitk
Stash Changes
# Stash tracked files, but NOT new files, NOT ignored files git stash # Stash with message git stash save "Add readme.txt" # Stash tracked files, new files, but NOT ignored files git stash -u # Stash with message. Note the save keyword git stash save -u "Add readme.txt" # Stash tracked files, new files AND ignored files git stash -a # Reapply stashed changes, also remove from stashed files git stash pop # Reapply stashed changes, also do NOT remove from stashed files git stash apply # You can stash multiple stashes. List all stashes git stash list # Reapply a specific stash git stash pop stash@{2}
Undo Things
Change or Redo Last Commit
# Redo last commit with new message git commit --amend -m "Redo commit" # Redo last commit with original commit message git commit --amend -C HEAD
* Example:
$ vi file1.txt $ git add file1.txt $ git ci -m "Add file1.txt" file1.txt [master 7e3524a] Add file1.txt 1 file changed, 1 insertion(+) create mode 100644 file1.txt $ git lg 7e3524a2c39be7aa02f6536bb05f86537cc8119f Add file1.txt $ vi file1.txt $ git ci --amend -m "Redo add file1.txt" file1.txt [master c25eb50] Redo add file1.txt 1 file changed, 2 insertions(+) create mode 100644 file1.txt $ git lg c25eb5041b5aa21ae240fbb379a9b8f27cb73f67 Redo add file1.txt
* Another Example
git commit -m 'initial commit' git add forgotten_file git commit --amend -C HEAD $ vi file1.txt $ git add file1.txt $ git commit -m "Add some files." [master f29da6b] Add some files. 1 file changed, 1 insertion(+) create mode 100644 file1.txt $ git lg f29da6be0b4f91575d1bedf4d82ce7c7eef1d248 Add some files. $ vi file2.txt $ git add file2.txt $ git commit --amend -C HEAD [master fdd5863] Add some files. 2 files changed, 2 insertions(+) create mode 100644 file1.txt create mode 100644 file2.txt $ git lg fdd58637e0cb8d56ad1a47438e8526afcd10292f Add some files.
Discard Commits
* Discard last commit
git reset HEAD~ $ git lg fdd58637e0cb8d56ad1a47438e8526afcd10292f Add some files. ea9e63cb37606b7901f5baa91c8c8628d967afa7 Add mylib2 $ git reset HEAD~ jiali@My /w/git/test3/my-proj (master) $ git lg ea9e63cb37606b7901f5baa91c8c8628d967afa7 Add mylib2
* Discard last three commits and resetting the branch tip to the fourth commit back:
git reset HEAD~3
Revert Changes
* Revert a modified file:
git checkout -- modified_file $ vi file1.txt $ git diff file1.txt diff --git a/file1.txt b/file1.txt index e212970..75ac157 100644 --- a/file1.txt +++ b/file1.txt @@ -1 +1,2 @@ file1 +second line $ git checkout -- file1.txt $ git diff file1.txt
* Revert all modified files:
git checkout .* Return to master branch
git checkout master* Checkout file1.txt from a particular commit number:
git checkout commit_number file1.txt* Checkout a particular commit
git checkout commit_numberWorking with Remotes
Show Remotes
git remote # list remote short name git remote -v # also show remote url
Add remote short name
git remote add alias_name remote_urlFetch/Pull from Remotes
git fetch remote_name git pull remote_name # fetch and merge
* Example:
git fetch originPushing to Remotes
git push remote_name branch_name* Example:
git push origin masterInspecting a Remote
git remote show originRename Remotes
git remote rename old_name new_nameRemove Remote
git remote rm remote_name
Branching
* Default branch: master
Create New Branch
# Create a new branch from current commit git checkout -b jimmy # Show current HEAD pointer $ git symbolic-ref HEAD refs/heads/jimmy # Create a new branch from specific commit git checkout -b jimmy 09d3cfad
Show Branches
* Show local branches only:
git branch git branch john master
* Show remote branches only:
git branch -r $ git branch -r origin/HEAD -> origin/master origin/john origin/master
* Show remote branches too:
$ git ls-remote origin 31104cf88172c94b60820d6d90739bd8ee391ccb HEAD 31104cf88172c94b60820d6d90739bd8ee391ccb refs/heads/john 31104cf88172c94b60820d6d90739bd8ee391ccb refs/heads/master
* Show all branches
git branch --all $ git branch --all * john master remotes/origin/HEAD -> origin/master remotes/origin/john remotes/origin/master
* Show local branches and last commits
git show-branch $ git show-branch * [john] Add john1.txt # Currently at HEAD branch john ! [master] Add john1.txt # Non-HEAD branch -- *+ [john] Add john1.txt # Last commit to john branch
* Show log graph
git log --graph --all --pretty=oneline $ git log --graph --all --pretty=oneline * 31104cf88172c94b60820d6d90739bd8ee391ccb Add file4.txt * 09d3cfadd21444f2da6d61a353e9da909a89d062 Add file3.txt | *-. 969e5ede4d747d2256eaaead70c05b0f14647ec4 On master: file4.txt | |\ \ |/ / / | | * 7db8a49ab0a76ac253da633aa2741cc6140f2a72 untracked files on master: 4a0f36 | * 5dae492d06bcdeadba4eddadb3ac4908a5688d6f index on master: 4a0f368 Add file2. |/ * 4a0f368da6cd21cf90c7281ccdf5bb806af41c7f Add file2.txt * 195d2c446d948717ab5fbfe882c4ae4c3e1b9e5e Add file1.txt
Switch Branch
* When switching,
– untracked files are ignored
– switching is aborted if untracked files already exist in target branch
— use git checkout –merge option to merge
# Switch to master branch git checkout master $ git symbolic-ref HEAD refs/heads/master # Switch to jimmy branch git checkout jimmy $ git symbolic-ref HEAD refs/heads/jimmy
Delete Branch
# Save delete a branch # Branch to be deleted needs to be fully merged git branch -d jimmy # Force delete a branch git bran -D jimmy
Renaming a Branch
git branch -m old new $ git branch -m jimmy john jiali@My /w/git/test3/my-proj (john) $ git branch -v * john 09d3cfa Add file3.txt master 4a0f368 [ahead 2] Add file2.txt
Push Branch to Remote
$ git push origin john Counting objects: 10, done. Delta compression using up to 2 threads. Compressing objects: 100% (6/6), done. Writing objects: 100% (9/9), 801 bytes, done. Total 9 (delta 2), reused 0 (delta 0) To file:///w/git/test2/my-proj.git * [new branch] john -> john
Merging
* Merge branch john to master:
git checkout master git merge john $ git checkout master Switched to branch 'master' Your branch is ahead of 'origin/master' by 2 commits. (use "git push" to publish your local commits) jiali@My /w/git/test3/my-proj (master) $ git merge john Updating 4a0f368..31104cf Fast-forward file3.txt | 1 + file4.txt | 1 + 2 files changed, 2 insertions(+) create mode 100644 file3.txt create mode 100644 file4.txt jiali@My /w/git/test3/my-proj (master)
Examples
Generate Patch Files
* Generate a single patch file named patch-083018.patch in home directory.
– The patch file contains past 22 commits.
git format-patch -22 --stdout > ~/patch-083018.patch
Issues
Couldn’t set refs/heads/master
* Error message:
$ git commit -m "Test" error: Couldn't set refs/heads/master fatal: cannot update HEAD ref
* Fix:
git fsck --lost-found # If still no luck # go to project root directory and issue: echo ref: refs/heads/master >.git/HEAD
File is far too short to be a packfile
* Env:
$ git version git version 1.8.1.msysgit.1
– Win 7
* Error message:
$ git status
Git error: ... is far too short to be a packfile* Fix:
– Close Git or Git GUI
– Close all opened folders, especially mounted drives
– Retry
References
* Pro Git
* Git Tutorial