Contents
<< Previous
Describe the structure and parts of a Java web application
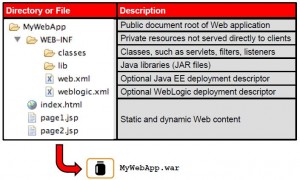
Web App
* Descriptors
– web.xml
– weblogic.xml
Web Services App
* Descriptors
– web.xml
– weblogic.xml
– webservices.xml
– weblogic-webservices.xml
Virtual Directory Mappings
* Used to refer to physical directories
* Used to avoid hard coding physical directories
* Allow multiple web apps to share common physical directories, e.g. images
* Promotes file sharing across applications
* Configured in weblogic.xml
<virtual-directory-mapping> <local-path>c:/usr/gifs</local-path> <url-pattern>/images/*</url-pattern> <url-pattern>*.jpg</url-pattern> </virtual-directory-mapping> <virtual-directory-mapping> <local-path>c:/usr/common_jsps.jar</local-path> <url-pattern>*.jsp</url-pattern> </virtual-directory-mapping>
Describe the structure and parts of a Java enterprise application
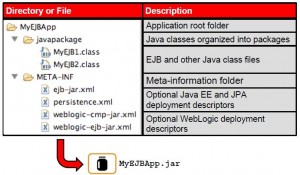
EJB Applications
* Server side distributed components
* Are annotated Java classes
* Packaged with XML deployment descriptors
* Supports the following capabilities
– remote access over a network
– object relational mapping (ORM) via JPA
– transactions
– messaging integration
– dependency injection
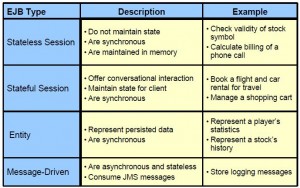
EJB Types
EJB App Structure
weblogic-ejb-jar.xml
* Security role mapping
* Advanced security role mapping
* EJB clustering
* EJB pooling and caching
* Work managers and threading
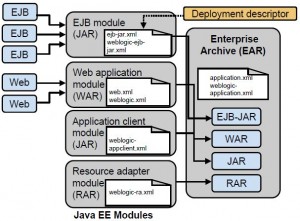
Enterprise Application
* A deployable unit packaged in an .ear file and contains zero or more:
– web apps (.war)
– EJB apps (.jar)
– Java apps (.jar)
– resource adapters (.rar)
– application specific JDBC and JMS resources
weblogic-application.xml
* Used to configure
– reference to shared libraries
– work managers and threading
– default EJB and web app parameter values
– application wide EJB cache
* Used to configure all web app modules:
– change default HTTP session timeout
– default cookie name used to track HTTP sessions
– enabling clustering features such as in-memory replication and persistence
* Used to achieve application scoping for:
– XML parsers
– XML entity mappings
– JDBC data sources
– JMS connection factories and destinations
– security realms (?)
EAR Class Libraries
* J2EE 1.4
– APP-INF/lib
– APP-INF/classes
* In J2EE 5, use library-directory to specify jars to be shared by all applications (default to lib?):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <application xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" version="5" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/application_5.xsd"> <module> <ejb>hello-ejb.jar</ejb> </module> <module> <web> <web-uri>hello.war</web-uri> <context-root>hello</context-root> </web> </module> <library-directory>shared</library-directory> </application>
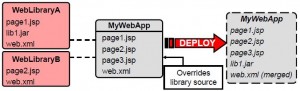
* For sharing J2EE modules (war, jar, ear)
* Local resources take precedence over shared ones
* Can contain deployment descriptors that are merged with application’s descriptors
* Configure shared libraries in weblogic.xml (for war) or weblogic-applicaiton.xml (for ear)
<library-ref> <library-name>ajax-tools-lib</library-name> <!-- J2EE version --> <specification-version>1.5.0</specification-version> <!-- Your implementation version --> <implementation-version>2.0.0</implementation-version> </library-ref> <library-ref> <library-name>help-web-lib</library-name> <specification-version>1.5.0</specification-version> <implementation-version>1.1.0</implementation-version> </library-ref>
Next >>
[mv_include id=’3268′]