Contents
- Overview
- Getting Started
-
Examples
- Print out Processes
- Print out DLLs Loaded
- Semicolons and Return keyword are Optional
- Data Types
- Exception Handling
- Quotes
- PowerShell Subexpression
- Here Strings
- Closures, Functions, and Lambdas
- Arrays
- Parentheses
- Hash Tables
- Get-Member
- Pipe to Grid View
- New-Object
- Add-Member
- Add-Type
- Modules
- Scan for Name Value Pairs
- Template Engines
- Generate PowerShell Functions From C# Methods
- Calling PowerShell Functions from C#
- References
Overview
* PowerShell is a glue language for distributed automation in Windows environment
* Leverage .NET framework
– Can be embedded in .NET applications
– Can embed .NET code directly in a PowerShell script
– Access C# class methods: [System.Math]::Pow(2,3)
* cmdlets are the basic units
* Pre-installed in Windows 7 and above
Getting Started
* Start PowerShell from Accessories -> Windows PowerShell menu folder
* Find version:
Windows PowerShell
Copyright (C) 2009 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
PS C:\Users\Jimmy> $PSVersionTable
Name Value
---- -----
CLRVersion 2.0.50727.4984
BuildVersion 6.1.7600.16385
PSVersion 2.0
WSManStackVersion 2.0
PSCompatibleVersions {1.0, 2.0}
SerializationVersion 1.1.0.1
PSRemotingProtocolVersion 2.1* As calculator:
PS C:\Users\Jimmy> 2 + 2 * 3 8 PS C:\Users\Jimmy> "Hello World" Hello World PS C:\Users\Jimmy> [System.Math]::Pow(2,3) 8
* Use variable:
PS C:\Users\Jimmy> $a = "hello" PS C:\Users\Jimmy> $a.GetType() IsPublic IsSerial Name BaseType -------- -------- ---- -------- True True String System.Object
Run Scripts
* Set-ExecutionPolicy
– Restricted (default): does not allow scripts or load config files
– AllSigned: all scripts must be signed
– RemoteSigned: remote scripts must be signed
– Unrestricted: no restriction
– Bypass: bypass all checks, even no warnings or prompts
– Undefined: remove currently assigned execution policy from the current scope except those in Group Policy scope
PS C:\Windows\system32> mkdir c:\temp
Directory: C:\
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
---- ------------- ------ ----
d---- 4/19/2013 4:11 PM temp
PS C:\Windows\system32> dir c:\temp
PS C:\Windows\system32> cd c:\temp
PS C:\temp> Set-ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted
PS C:\temp> Get-Content .\test.ps1
"Hello World"
PS C:\temp> .\test.ps1
Hello World
PS C:\temp>PowerShell Editors
* PowerShell ISE (built-in)
* PowerGUI
* PowerShell Analyzer
* Professional PowerShell Script Editor (PowerSE)
* PrimalScript
* PowerShell Plus
* Visual Studio Plugins:
– NuGet
– StudioShell
Special Variables
$_ – Contains the current pipeline object, used in script blocks, filters, and the where statement.
$Args – Contains an array of the parameters passed to a function.
$Error – Contains objects for which an error occurred while being processed in a cmdlet.
$Home – Specifies the user’s home directory.
$PsHome – The directory where the Windows PowerShell is installed.
Special characters
* #: Comment character
# This is a comment
* %: is an alias for ForEach
* ?: is an alias for Where
1..10 | ? {$_ % 2 -eq 0} | % {$_* 2}
4
8
12
16
20Set-Aliase
Set-Alias np "C:\Program Files (x86)\Notepad++\notepad++.exe" np
Examples
Print out Processes
PS C:\temp> Get-Process | Where {$_.Handles -gt 750} | Sort PM -Descending
Handles NPM(K) PM(K) WS(K) VM(M) CPU(s) Id ProcessName
------- ------ ----- ----- ----- ------ -- -----------
979 211 1154988 1204292 1755 ...70.65 5168 firefox
986 36 309332 327200 507 4,377.56 1688 svchost
1208 117 159196 176844 542 108.06 9228 VpxClient
1685 61 154912 128292 585 9,778.64 4508 FlashPlayerPlugin_11_6_602_180
1477 105 107580 224284 563 1,144.64 5328 explorer
2409 57 58104 89468 510 127.56 1728 svchost
1003 58 45220 23216 290 278.49 9456 avgui
824 49 42332 45240 632 43.27 1144 svchost
1357 27 38520 45224 147 541.70 2028 avgrsa
880 25 38184 30512 210 610.51 1140 csrss
823 50 23032 38368 113 18.77 1872 svchost
755 17 18516 42500 123 43.84 2136 nvxdsync
942 38 15232 29568 146 1,090.90 5792 avgwdsvc
993 30 13300 30016 133 1,989.00 3296 AcSvc
944 31 12444 58312 84 227.12 1212 lsass
857 16 4092 15068 123 11.95 772 csrss
1103 10 2600 6712 53 1.45 2596 CamMute
1435 0 424 10816 143 4 SystemPrint out DLLs Loaded
PS C:\temp> [System.AppDomain]::CurrentDomain.GetAssemblies() |
>> Where {$_.location} |
>> ForEach { Split-Path -Leaf $_.location } |
>> Sort
>>
Microsoft.PowerShell.Commands.Diagnostics.dll
Microsoft.PowerShell.Commands.Management.dll
Microsoft.PowerShell.Commands.Utility.dll
Microsoft.PowerShell.ConsoleHost.dll
Microsoft.PowerShell.Security.dll
Microsoft.WSMan.Management.dll
mscorlib.dll
System.Configuration.Install.dll
System.Core.dll
System.Data.dll
System.DirectoryServices.dll
System.dll
System.Management.Automation.dll
System.Management.dll
System.Transactions.dll
System.Xml.dllSemicolons and Return keyword are Optional
PS C:\temp> function SayHello($p) {
>> return "Hello $p"
>> }
>>
PS C:\temp> SayHello World
Hello World
PS C:\temp> function SayHello($p) {
>> "Hello $p"
>> }
>>
PS C:\temp> SayHello World
Hello WorldData Types
PS C:\temp> $a = "Hello"
PS C:\temp> $a
Hello
PS C:\temp> $a = 1
PS C:\temp> $a += 1
PS C:\temp> $a
2
PS C:\temp> $a = 1,2,3
PS C:\temp> $a
1
2
3
PS C:\temp> [int]$a = 1
PS C:\temp> $a
1
PS C:\temp> [int]$a = "Hello"
Cannot convert value "Hello" to type "System.Int32". Error: "Input string was not in a correct format."
At line:1 char:8
+ [int]$a <<<< = "Hello"
+ CategoryInfo : MetadataError: (:) [], ArgumentTransformationMetadataException
+ FullyQualifiedErrorId : RuntimeException* Strong typed parameters:
PS C:\temp> function Do-PrecisionCalculation {
>> param (
>> [Double]$Latitude,
>> [Double]$Longitude
>> )
>>
>> [Math]::Sin($Latitude) * [Math]::Sin($Longitude)
>> }
>>
PS C:\temp> Do-PrecisionCalculation -Latitude 100 -Longitude 100
0.256406162496497Exception Handling
* Supports try/catch/finally:
PS C:\Users\Jimmy> function div-by-zero($a, $b){
try {
$a/$b
"Hello World"
} catch {
"Error caught: $($error[0])"
} finally {
"Finally, Hello World"
}
}
PS C:\Users\Jimmy> div-by-zero -a 1 -b 0
Error caught: Attempted to divide by zero.
Finally, Hello WorldQuotes
PS C:\temp> PS C:\temp> "A string" A string PS C:\temp> PS C:\temp> "A string with 'Quotes'" A string with 'Quotes' PS C:\temp> PS C:\temp> "A string with `"Escaped Quotes`"" A string with "Escaped Quotes" PS C:\temp> PS C:\temp> $s = "PowerShell" PS C:\temp> "A string with a variable: $s" A string with a variable: PowerShell PS C:\temp> PS C:\temp> "A string with a quoted variable: '$s'" A string with a quoted variable: 'PowerShell' PS C:\temp> PS C:\temp> 'Variables are not replaced inside single quotes: $s' Variables are not replaced inside single quotes: $s
PowerShell Subexpression
PS C:\temp> $process = (Get-Process)[0] PS C:\temp> $process.PM 6443008 PS C:\temp> "$process.PM" System.Diagnostics.Process (AcDeskBandHlpr).PM PS C:\temp> "$($process.PM)" 6443008
Here Strings
$name = "World" $HereString = @" This is a here-string It can contain multiple lines "Quotes don't need to be escaped" Plus, you can include variables 'Hello $name' "@ PS C:\Users\Jimmy> $HereString This is a here-string It can contain multiple lines "Quotes don't need to be escaped" Plus, you can include variables 'Hello World'
Closures, Functions, and Lambdas
* Closures:
– surrounded by {}
– executed by & operator
PS C:\temp> $n = "PowerShell"
PS C:\temp> $closure = {"Hello $n"}
PS C:\temp> & $closure
Hello PowerShell
PS C:\temp>* Functions (closures or script blocks with names):
PS C:\temp> function Add5 ($num) {
>> $num + 5
>> }
>>
PS C:\temp> Add5 5
10* Lambdas (closures or script blocks without names):
PS C:\temp> $add5 = {param($num) $num + 5}
PS C:\temp> & $add5 5
10Arrays
* Same as .NET System.Array
$animals = "cat", "dog", "fish" $animals.GetType() $animals IsPublic IsSerial Name BaseType -------- -------- ---- -------- True True Object[] System.Array cat dog fish
* Empty array:
$animals = @() $animals.Count 0
* Add an array item:
$animals = "cat", "dog", "fish" $animals += "bird" $animals cat dog fish bird
* Access an array item:
$animals = "cat", "dog", "fish" $animals[1]
* Array slicing:
$animals = "cat", "dog", "fish" $animals[0..1] cat dog
* Finding array elements:
$animals = "cat", "dog", "fish" $animals -ne 'cat' dog fish $animals = "cat", "dog", "fish" #$animals -ne 'cat' $animals -like "*o*" dog
* Reversing an array:
$animals = "cat", "dog", "fish" [array]::Reverse($animals) $animals fish dog cat
* Assign array values to multiple variables
$items = "One", "Two", "Three", 1, 2, 3 $items $one, $two, $three, $numbers = $items $one $two $three $numbers One Two Three 1 2 3 One Two Three 1 2 3
Parentheses
* Don't use parentheses to pass parameters to a function:
function Test($p1, $p2) {
'$p1' + "is: " + $p1
'$p2' + "is: " + $p2
""
}
Test (1, 2) # Actually passing in an array
Test 1 2
$p1is: 1 2
$p2is:
$p1is: 1
$p2is: 2Hash Tables
# Empty hash map
$h = @{}
$h.Count
# Assign elements
$h.Item1 = 1
$h.Item2 = 2
# Initialize hash map
$h = @{Item1=1; Item2=2}
# Access hash map
$h
$h.Item1
$h.Item2
# Concatenate hash tables
$h1 = @{a=1;b=2}
$h2 = @{c=3;d=4}
$h = $h1 + $h2
$hGet-Member
* Returns the members (properties and methods) of objects at the command line.
New-Object Net.Webclient | Get-Member -MemberType Property
TypeName: System.Net.WebClient
Name MemberType Definition
---- ---------- ----------
BaseAddress Property System.String BaseAddress {get;set;}
CachePolicy Property System.Net.Cache.RequestCachePolicy CachePolicy {get;set;}
Container Property System.ComponentModel.IContainer Container {get;}
Credentials Property System.Net.ICredentials Credentials {get;set;}
Encoding Property System.Text.Encoding Encoding {get;set;}
Headers Property System.Net.WebHeaderCollection Headers {get;set;}
IsBusy Property System.Boolean IsBusy {get;}
Proxy Property System.Net.IWebProxy Proxy {get;set;}
QueryString Property System.Collections.Specialized.NameValueCollection QueryString {get;set;}
ResponseHeaders Property System.Net.WebHeaderCollection ResponseHeaders {get;}
Site Property System.ComponentModel.ISite Site {get;set;}
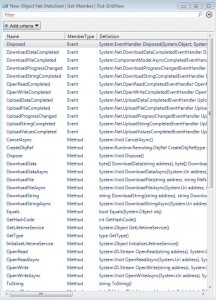
UseDefaultCredentials Property System.Boolean UseDefaultCredentials {get;set;}Pipe to Grid View
New-Object Net.Webclient | Get-Member | Out-GridView
New-Object
* Creates an instance of .NET object
* Examples:
– Open IE and go to google.com:
$ie = New-Object -ComObject InternetExplorer.Application
$ie.Navigate2("http://www.google.com")
$ie.Visible = $true– Create a new PowerShell object:
$obj = New-Object PSObject -Property @{Name="John";Age="10"}
$obj.GetType()
$obj
IsPublic IsSerial Name BaseType
-------- -------- ---- --------
True False PSCustomObject System.Object
Name : John
Age : 10– Use .NET framework:
$wc = New-Object Net.WebClient
[xml]$resp = $wc.DownloadString("http://feeds.feedburner.com/DevelopmentInABlink")
$resp.rss.channel.item | ForEach {$_.Title}
PowerShell Automation
Creating a PowerShell Translate Function
How to run PowerShell from node.js
Using PowerShell to find all the years since you were born where the four digits were unique
Use PowerShell to find the free space on the volume behind an SMB file share
Learn one PowerShell command
I’ll be presenting on PowerShell at the Philly Code Camp
Building GUI Applications in PowerShell
Honorary PowerShell Scripting Guy
PowerShell kv – save snippets of text that you can later find and copy to your clipboardAdd-Member
$s = "Hello World" | Add-Member -PassThru ScriptProperty Reverse {$this[$this.Length..0] -join ""}
$s
$s.Reverse
Hello World
dlroW olleHAdd-Type
* Compile C# on the fly:
Add-Type -TypeDefinition @"
public class MyMathClass {
public int Add(int n1, int n2) {
return n1 + n2;
}
}
"@
$obj = New-Object MyMathClass
$obj.GetType()
$obj | Get-Member
1..5 | ForEach {$obj.Add($_,$_)}Modules
TODO.
Scan for Name Value Pairs
$regex = "(?<name>\w+)\s*=\s*(?<value>.*)((?=\W$)|\z)"
dir c:\temp *.txt | Select-String $regex |
ForEach {
$fn = $_.Path
ForEach($match in $_.Matches) {
$obj = New-Object PSObject -Property @{
FileName = $fn
Name = $match.Groups["name"].Value
Value = $match.Groups["value"].Value
}
}
$obj
}Template Engines
* Process templates and content to produce output
TODO
Generate PowerShell Functions From C# Methods
* MyMath C# class:
$code = @"
public class MyMath {
public int MyAdd(int n1, int n2) {
return n1 + n2;
}
public int MySubstract (int n1, int n2) {
return n1 - n2;
}
}
"@
Add-Type -TypeDefinition $code
[MyMath].GetMethods()
[MyMath].GetMethods() |
ForEach {
$_.GetParameters()
}* PowerShell Wrapper:
$MyMath = New-Object MyMath
function Invoke-MyAdd ($n1, $n2) {$MyMath.MyAdd($n1, $n2)}
function Invoke-MySubstract ($n1, $n2) {$MyMath.MySubstract($n1, $n2)}
Invoke-MyAdd 1 3
1..10|
ForEach {Invoke-MyAdd $_ $_}* Note that once type is added, it can not be removed until you restart PowerShell
Calling PowerShell Functions from C#
TODO
References
* Windows PowerShell for Developers