WebLogic 11g: Deploying with weblogic.Deployer
Uploading Deployment Files from a Remote Client
java weblogic.Deployer \
-adminurl http://localhost:7001 \
-username weblogic \
-password weblogic \
-deploy \
-upload \
c:\localfiles\myapp.ear* Uploaded to server’s upload directory (defaults to ?).
Deploying to a Single-Server Domain
java weblogic.Deployer \
-adminurl http://localhost:7001 \
-username weblogic \
-password weblogic \
-deploy \
-name myTestApplication \
c:\localfiles\myapp.ear
Deploying an Application with a Deployment Plan
java weblogic.Deployer \
-adminurl http://localhost:7001 \
-username weblogic \
-password weblogic \
-deploy \
-name myTestDeployment \
-source /myDeployments/installedApps/myApplication/app/myApplication.ear \
-targets myCluster \
-stage \
-plan /myDeployments/installedApps/myApplication/plan/plan.xml
Deploying an Application That Looks Up System Resources from JNDI During preStart
* Create and activate desired system resources in a separate session before deploy the application that relies on it.
Targeting Deployments to Servers, Clusters, and Virtual Hosts
* Deploy to sinple target:
java weblogic.Deployer \
-adminurl http://localhost:7001 \
-username weblogic \
-password weblogic \
-deploy \
-targets companyHost c:\localfiles\myWebApp.ear
* Deploy to more than one targets:
java weblogic.Deployer \
-adminurl http://localhost:7001 \
-username weblogic \
-password weblogic \
-deploy \
-targets ManagedServer-1,ManagedServer-2 \
c:\localfiles\myapp.ear* Deploy to a cluster target:
– To enforce strict deployment for all servers configured in a cluster:
-DClusterConstraintsEnabled=true
Using Module-Level Targeting for Deploying an Enterprise Application
Target individual modules in an enterprise application
java weblogic.Deployer \
-adminurl http://localhost:7001 \
-username weblogic \
-password weblogic \
-name myEnterpriseApp \
-targets module1@myserver1,module2@myserver2,module3@myserver3 \
-stage \
-deploy c:\localfiles\myEnterpriseApp.ear
Targeting Web Application Modules
– To target Web application modules that are part of an .ear file, you can use the Web application’s context-root name as the module name or specify the web-uri.
– If
<module>
<web>
<web-uri>myweb.war</web-uri>
<context-root>/welcome</context-root>
</web>
</module>You can use context-root:
java weblogic.Deployer \
-adminurl http://localhost:7001 \
-username weblogic \
-password weblogic \
-name mywebapplication \
-targets /welcome@myserver1 \
-stage \
-deploy c:\localfiles\myEnterpriseApp.ear
Or web uri:
java weblogic.Deployer \
-adminurl http://localhost:7001 \
-username weblogic \
-password weblogic \
-name mywebapplication \
-targets myweb.war@myserver1 \
-stage \
-deploy c:\localfiles\myEnterpriseApp.ear
– For default context root, i.e. ‘/’
<module>
<web>
<web-uri>myweb.war</web-uri>
<context-root>/</context-root>
</web>
</module>Then only
java weblogic.Deployer \
-adminurl http://localhost:7001 \
-username weblogic \
-password weblogic \
-name mywebapplication \
-targets /@myserver1 \
-stage \
-deploy c:\localfiles\myEnterpriseApp.ear
Deploying JDBC, JMS, and WLDF Application Modules
* Only available to the server to which they are targeted.
– Need to target to multiple servers or cluster to be available on them.
Targeting Application-Scoped JMS, JDBC, and WLDF Modules
* Application-scoped resource modules can be targeted independently of other EAR modules during deployment, if necessary, by using module-level targeting syntax.
* For example:
java weblogic.Deployer
-adminurl http://localhost:7001
-username weblogic
-password weblogic
-name myEnterpriseApp
-targets myWebApp@myCluster,myJDBCModule@myserver1,myEJBModule@myserver1
-stage
-deploy c:\localfiles\myEnterpriseApp.ear
Sub-module Targeting for Standalone JMS Modules
* For a standalone JMS module, the submodule targeting syntax is: -submoduletargets submodule_name@target_name.
* For example, to deploy a standalone JMS module on a single server instance, targeting the submodule myQueue to a JMS Server named JMSServer1, enter the command:
java weblogic.Deployer -adminurl http://localhost:7001 -username weblogic
-password weblogic -name myJMSModule
-targets ManagedServer1 -submoduletargets myQueue@JMSServer1
-deploy c:\localfiles\myJMSModule.xml
* To undeploy the same JMS module, enter the following command, which, assuming myJMSModule contains more than one submodule, will undeploy only the myQueue submodule; all other submodules are unaffected.
java weblogic.Deployer -adminurl http://localhost:7001 -username weblogic
-password weblogic -name myJMSModule
-undeploy -submoduletargets myQueue@JMSServer1
Sub-module Targeting for Application-scoped JMS Modules
* For an application-scoped JMS module in an EAR, use the syntax: submodule_name@module_name@target_name to target a submodule.
* For example, if the queue in the above example were instead packaged as part of an Enterprise application, you would use the command:
java weblogic.Deployer -adminurl http://localhost:7001 -username weblogic
-password weblogic -name myEnterpriseApp
-targets ManagedServer1 -submoduletargets myQueue@myJMSModule@JMSServer1
-deploy c:\localfiles\myEnterpriseApp.ear
* To undeploy the same JMS module, enter the following command, which, assuming myEnterpriseApp contains more than one submodule, will undeploy only the myQueue submodule; all other submodules are unaffected.
java weblogic.Deployer -adminurl http://localhost:7001 -username weblogic
-password weblogic -name myEnterpriseApp
-undeploy -submoduletargets myQueue@myJMSModule@JMSServer1
Deployment Stage Modes
* Determines how deployment files are made available to target servers that must deploy an application or standalone module.
* WebLogic Server provides three different options for staging files:
– stage mode,
– nostage mode,
– external_stage mode.
nostage Mode
* The Administration Server does not copy deployment unit files.
* Stage directory is ignored.
* Instead, all servers deploy using the same physical copy of the deployment files, which must be directly accessible by the Administration Server and target servers.
* With nostage deployments of exploded archive directories, WebLogic Server automatically detects changes to a deployment’s JSPs or Servlets and refreshes the deployment. (This behavior can be disabled if necessary.)
* Default mode used by Admin Console to deploy only to Admin Server.
* Use when
– Deploying to a single-server domain.
– Deploying to a cluster on a multi-homed machine.
– Deploying very large applications to multiple targets or to a cluster where deployment files are available on a shared directory.
– Deploying exploded archive directories that you want to periodically redeploy after changing content.
– Deployments that require dynamic update of selected Deployment Descriptors via the Administration Console.
* Syntax
java weblogic.Deployer
-adminurl http://localhost:7001
-username weblogic
-password weblogic
-name mydeploymentname
-targets myserver1,myserver2,myserver3
-nostage
-deploy c:\localfiles\myapp.earstage Mode
* The Administration Server first copies the deployment unit source files to the staging directories of target servers.
– The staging directory is named stage by default, and it resides under the target server’s root directory.
* When copying files to the staging directory, the Administration Server creates a subdirectory with the same name as the deployment name.
* The target servers then deploy using their local copy of the deployment files.
* stage mode is the default mode for:
– Administration Console when deploying to more than one WebLogic Server instance.
– Managed Servers.
– weblogic.Deployer uses the target server’s staging mode as the default,
* Use when:
– Deploying small or moderate-sized applications to multiple WebLogic Server instances.
– Deploying small or moderate-sized applications to a cluster.
* Syntax:
java weblogic.Deployer -adminurl http://localhost:7001 -username weblogic
-password weblogic -name mydeploymentname
-targets myserver1,myserver2,myserver3 -stage
-deploy c:\localfiles\myapp.ear
external_stage Mode
* Similar to stage mode, i.e. target servers deploy apps using local copies of deployment files.
* You have to copy files to each target server’s staging directory manually.
– Deployment files must be stored in a subdirectory that reflects the deployment name.
cd WL_HOME/stage
mkdir myEARExternal/2.0Beta
cp myear myEARExternal/2.0Beta
* Use when you deploy very large applications to multiple machines and
– do not have a shared file system
– cannot use nostage mode
* Use the -noversion option to turn off the requirement that deployment files be on the Administration Server, but the -noversion option causes versioning information to be ignored so you cannot use the -noversion option with versioned applications.
* Syntax:
java weblogic.Deployer -adminurl http://localhost:7001 -name weblogic
-password weblogic -external_stage -name myEARExternal
-deploy c:\myapps\myear
Changing the Default Staging Behavior for a Server
* The server staging mode specifies the default deployment mode for a server if none is specified at deployment time, e.g. weblogic.Deployer.
* You can only change the server staging mode by using the Administration Console or by directly changing the ServerMBean via JMX.
* Changing the server staging mode does not affect existing applications.
– If you want to change the staging mode for an existing application, you must undeploy the application deployment and then redeploy it with the new staging mode.
* How to change
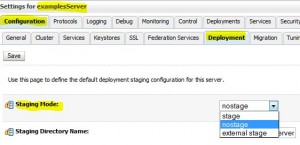
Distributing Applications to a Production Environment
Overview
* Copy application deployment files to all target servers and validate it.
* Application can be started in Admin mode after distribution (use the -adminmode option).
Syntax
java weblogic.Deployer -adminurl http://localhost:7001 -username weblogic
-password weblogic -distribute -name myTestDeployment
/myDeployments/myApplication/Start Application in Admin Mode
* Restricts access to the application to a configured Administration channel.
* Allows you to distribute the application or new version to a production environment without opening the application to external client connections.
* Need to configure an administration channel.
* Start a Distributed Application in admin mode:
java weblogic.Deployer -adminurl http://localhost:7001 -username weblogic
-password weblogic -start -adminmode -name myTestDeployment
/myDeployments/myApplication/* Starting a Distributed Application for new client connections:
java weblogic.Deployer -adminurl http://localhost:7001 -username weblogic
-password weblogic -start -name myTestDeploymentDeploying Shared Java EE Libraries and Dependent Applications
* A Java EE library is
– a standalone Java EE module,
– multiple Java EE modules packaged in an Enterprise application (EAR),
– or a plain JAR file that is registered with the Java EE application container upon deployment.
* After a Java EE library has been registered, you can deploy Enterprise applications that reference the library.
* Each referencing application receives a copy of the shared Java EE library module(s) on deployment (merging), and can use those modules as if they were packaged as part of the application itself.
* Need to redeploy all referencing applications after new version of library is deployed.
* Deploy as a library:
java weblogic.Deployer -adminurl http://localhost:7001 -username weblogic
-password weblogic -deploy -targets myserver1,myserver2
-library /deployments/myLibraryApplication/* Should always specify a libary version number:
– in manifest file
– use libspecver and/or libimplver options.
java weblogic.Deployer -adminurl http://localhost:7001 -username weblogic
-password weblogic -deploy -targets myserver1,myserver2
-library -libspecver 700 -libimplversion 7.0.0.1Beta
/deployments/myLibraryApplication/* Deploying applications that reference libraries as ususal.
– All referenced libraries are registered on the application’s target servers.
– Registered libraries meet the version requirements of the referencing application.
[mv_include id=”3569″]
* weblogic.Deployer Command-Line Reference

